
– Configure a new Sub-Interface on R1 to match the VLAN 30 (Fa0/0.30) and configure the sub-interface to use 802.1q encapsulation and the Dot1q tag of 30. To enable the sub-interface to use 802.1q you’ll use the encapsulation dot1q # command whereas # is the dot1q VLAN tag as shown below Įnter configuration commands, one per line. To create a new sub-interface you’ll use the interface fa0/0.# command in global configuration mode. Configure the sub-interface to use the IP address 10.1.20.1/24. – Configure a new Sub-Interface on R1 to match the VLAN 20 (Fa0/0.20) and configure the sub-interface to use 802.1q encapsulation and the Dot1q tag of 20. Verify that R2 can ping R3’s FastEthernet0/0 interface using R1 as the default-gateway.Disable IP Routing on R2 and R3 and configure the default gateway on R2 and R3 to use R1’s respected Sub-interface as the default gateway.

Configure the sub-interface to use the IP address 10.1.30.1/24. Configure a new Sub-Interface on R1 to match the VLAN 30 (Fa0/0.30) and configure the sub-interface to use 802.1q encapsulation and the Dot1q tag of 30.Configure a new Sub-Interface on R1 to match the VLAN 20 (Fa0/0.20) and configure the sub-interface to use 802.1q encapsulation and the Dot1q tag of 20.This command can be executed from user or privileged mode to view the current IP addresses of all interfaces on the device. This command is executed in global configuration mode to configure a non-routing device to use the specific IP Address as a default-gateway.
#How to configure router on a stick windows
This command is executed from global configuration and disables the routers ability to be used as a router, effectively turning it into a test client machine like a windows box. This command is executed from ethernet sub-interface configuration mode and binds the sub interface(s) to a particular 802.1q tagged vlan. In this lab you’ll familiarize yourself with the following new commands Command In this lab you’ll use sub-interfaces to match the VLAN’s in the trunk to allow for interfaces in each VLAN and accomplish inter-vlan routing for the hosts as the router has an interface in each layer three network. A sub-interface allows you to have multiple interface configurations on a single physical interface. 802.1q trunk interfaces carry all VLAN traffic.Ī single Router can utilize an 802.1q trunk link to place a sub-interface in each VLAN using a single physical link and technically have interfaces in all VLAN’s.Ī Sub-Interface is a logical interface partitioned off from a physical interface. Think back to the previous lab discussing Dot1q trunk interfaces.
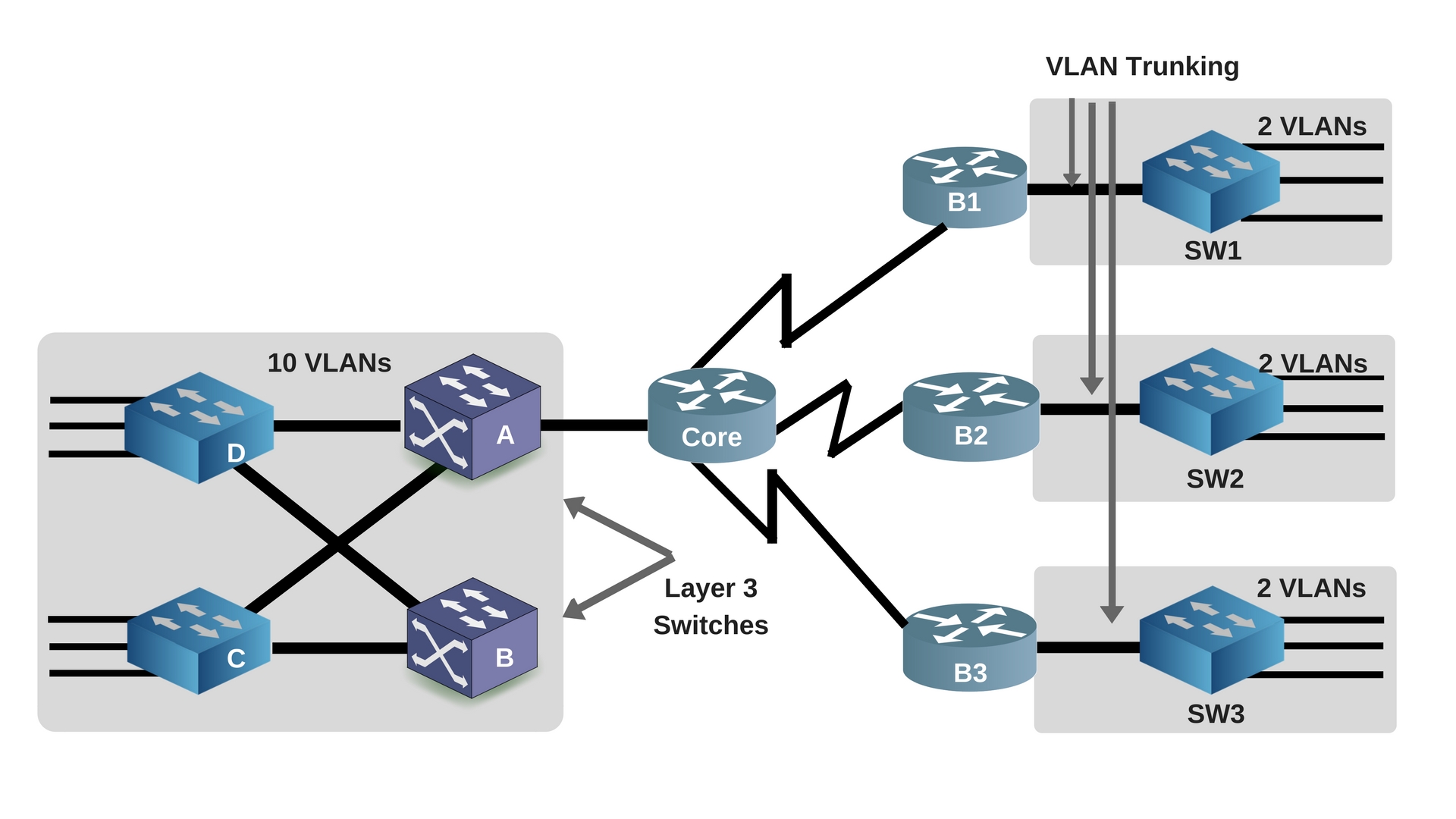
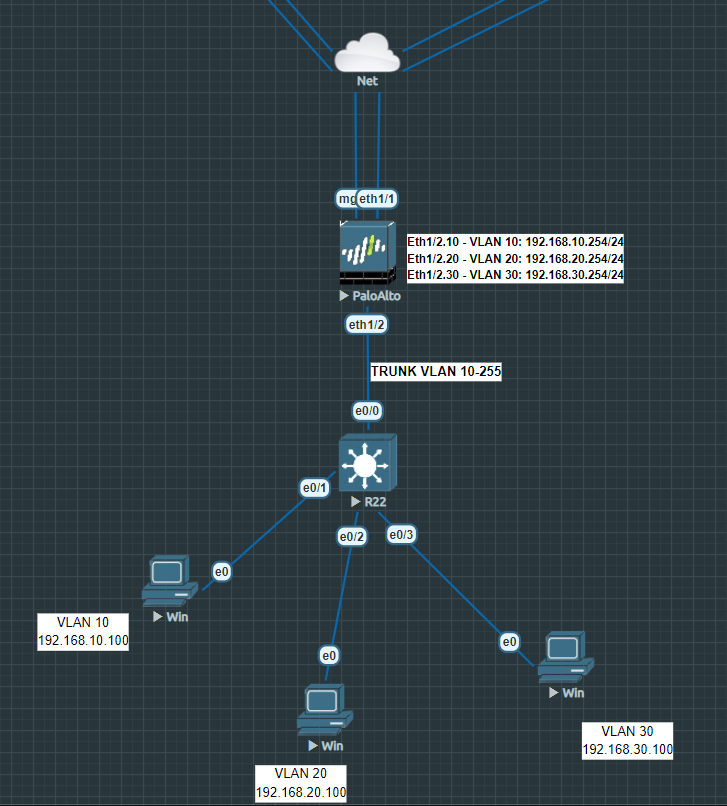
In this case you only need a SINGLE router and that’s it. The answer is easier then you’d initially think. So does this mean that multiple routers are required or a router with 5 physical ethernet interfaces, one interface in each VLAN? So let’s say for example you have a single switch with 5 different VLAN’s and machines on each VLAN in which case each VLAN would require its own router to get out of that layer two network to a different layer two network. The only way to get off a layer two network segment is through a layer three device commonly referred to as a Default Gateway for host machines.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
